Use Cases for AI in Higher Education
The Great Opportunities of Artificial Intelligence (AI)

IMAGE: DALL·E 3 via Copilot, prompt: “a computerized brain in the style of steampunk” (11/08/23).
AI and Formative Assessment
For our learners, how best can Artificial Intelligence serve them? One widely-held belief is that AI serves as an excellent tool for formative assessments.
While the definition below takes an instructor’s perspective, the emphasis of formative assessment’s role in the learning process is to help students better understand and master concepts, skills, and applications they may be struggling with.
Formative assessment can be defined as: “Formative assessment provides feedback and information during the instructional process, while learning is taking place, and while learning is occurring. Formative assessment measures student progress but it can also assess your own progress as an instructor. For example, when implementing a new activity in class, you can, through observation and/or surveying the students, determine whether or not the activity should be used again (or modified). A primary focus of formative assessment is to identify areas that may need improvement. These assessments typically are not graded and act as a gauge to students’ learning progress and to determine teaching effectiveness (implementing appropriate methods and activities).” Source: Northern Illinois University, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
Formative assessment can include, but are not limited to:
- Observations during in-class activities
- Homework exercises
- Class discussions
- Reflections journals
- Question and answer sessions
- Conferences between teacher and student
- In-class activities where students present their results
- Student feedback about instruction
Source: Northern Illinois University, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
Approaches to AI Formative Assessments
In the context of AI-supported learning, students can use AI to:
- Rewriting advanced passages so they are more appropriate to a given reading level
- Breaking down and/or rephrasing difficult concepts into manageable parts
- Rewriting or restating content that uses specialized vocabulary
- Clarifying homework directions (and/or materials necessary to complete homework assignments)
- Quizzing for understanding
- Reviewing in preparation for summative assessments
- Feedback: whether during content review or when drafting work for formal submission to an instructor
- Insights on how to evaluate peer work
- Sharing evaluative and constructive insights on performance improvement
- Translating
Successful Prompting
Students can harness the robust applications of AI through prompting. Writing a useful prompt is referred to as “prompt engineering”
Prompt engineering is the process of writing, refining, and optimizing inputs to guide generative AI systems to create specific, high-quality outputs. Source: IBM: What Is Prompt Engineering?
AI for Research
Bard
- Bard can now double-check any of its chatbot responses using Google Search. Chabot output is compared to online content – content that can either support or counter its conclusions. (This is not foolproof: Bard can still generate irrelevant information, suffer from hallucinations, or share inaccuracies.) But, shared sources can be followed-up on independently
- Enter a prompt and at the bottom of the prompt response click the Google icon to launch the double-check feature
- When the check is complete, content is differentiated according to color
- Click “Understand the results” for an explanation of variations in content reliability
- Click on a statement/sentence within the response and Google reveals the source
- Students can share their AI work with faculty
- The student can choose how much is shared
- A public link to share is created; anyone who gets this link can read the chat, take part in the chat, and share the chat after signing in to Google
Bing
- Bing Chat (reportedly) uses ChatGPT 4.0 architecture and is a web-based chatbot integrated into the Bing search engine and built into the Edge browser – giving it access to the Internet, unlike ChatGPT 3.5 which is not connected to the Internet
- The Chat window shares direct links to online sources within the response to a prompt
Perplexity
- Perplexity is a web-based chatbot that shares multiple sources in response to a prompt
- A user can click on the numbers within the response to directly visit an online source or use the source tiles above
- Users can also engage a “Copilot” for additional queries
- Copilot asks a user to log in to their Google or Apple account, or provide an email address
- If Copilot is engaged, a user is limited in the number of prompts/hour
- The Copilot delivers a more expansive response along the same lines as the standard version
AI Research Tools
- Elicit: Conduct academic research, collect sources, and interact with material via AI
- Research Rabbit: Conduct academic research, collect sources, and interact with material via AI
AI for Improving Accessibility
AI-supported tools do not replace specialized assistive technologies, but they do add an additional degree of accessibility and support.
The readily-available, free, and mainstream nature of their functionality is important in light of the fact that only 1/3 of college students with a disability share that with their institutions (NCES, 2022).
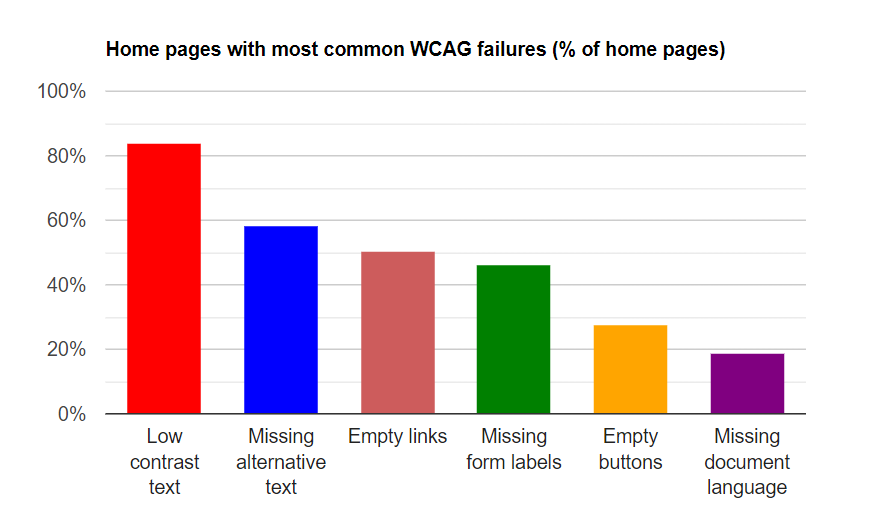
In the WebAim Million report, WebAIM (web accessibility in mind) assessed the degree of user accessibility for the most popular million homepages and web domains.
The table shared above outlines the most commonly recorded shortcomings in 2023: low-contrast text and the lack of alternative text. Low contrast text implies the color contrast between the text and a page is not significant enough for individuals with low vision/colorblindness; alternative text is a brief written description of an image that screen readers can read.
Learn how AI features can foster learner accessibility and promote student success.
