Quick Search’s results page contains elements that tell you more about the items you found. Here are some particularly useful ones to make note of:
Material type
Each item on your list has information to tell you what format your item is in, for example whether it is a book, journal article, or video. This is helpful when you are seeking a specific format (e.g. when your instructor requires a specific number of source formats, like one book and four journal articles). It also signals whether you can expect the resource to be long or short, or whether it is text-based or audio-visual.

Multiple versions exist
This indicates your search has found something with more than one edition or format. You can click either the title or the see all versions link to find the list of versions. This might be helpful when you’re looking for a specific edition of a book or specific recording of a musical piece. Think of Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet. In this case, “multiple versions” includes several different film versions, music recordings, different editions of books, physical books and e-books, and more.

Available or Checked out
This shows whether an item is available for you to use, or if it is not available to you because it is checked out.


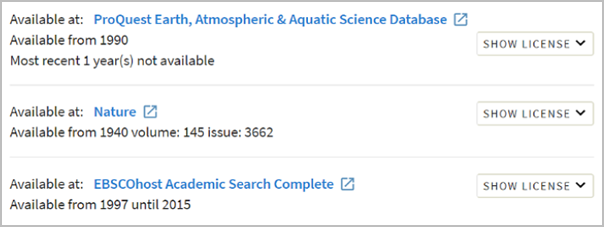
Full text available
This means the whole item, not just a snippet or excerpt, is available in a digital format. Clicking on online access or full text available takes you either directly to your item, or to the digital collection that includes your item. If there is more than one digital collection listed, check which years are displayed for each and select one that includes the year you need (when your resource was published).
Tweak my results
On the right side of your search result page you’ll find a number of filters that will help you focus your results. We’ll talk about them in more detail later; however, it is worth noting that they can be helpful at any stage of the search process. Some filters you might start using right away are availability (whether something is available online or in the library), format type, creation date, and topic.
Using Quick Search to locate library materials
Quick Search helps you find both electronic and physical items within the library. Electronic items usually have one or more links which allow access to the item. To locate a physical item, you need these three things: collection, location (Map it), and call number.

Collection
To find a physical item in the library, first check which collection your item is in. Collections you might encounter include:
- General Collection: Most library materials fall within this collection. These can be located on the Lower Level, Floors 2 and 3, and Tiers 1 through 7 of the library. You can find maps of the floors and tiers on the library website.
- Media Center: Located on the Lower Level, this collection includes DVDs, CDs, and other multimedia items.
- Special Collections: This department is home to rare and unique research materials that support major research areas of Iowa State University. Because these materials are rare and tend to be fragile, access is more restricted and hours are limited. Special Collections is located on Floor 4.
- Other locations, such as Design, Veterinary Medical Library, or the Storage Building may also be listed with the call number.
Location (Map it)
Some collections are spread across multiple floors, so Quick Search’s Map it can help. This feature indicates where your item is located in Parks Library. Map it lists the floor or tier your item should be on, and provides a graphic indicating the approximate location. If you need help locating your items you can always ask for assistance at the Main Desk.

Call numbers
Each item in the library has a unique call number. Like most academic research libraries in the United States, the ISU Library uses the Library of Congress Classification System to organize its books and journals. The first thing you need to know about this system is that it is alphanumeric, meaning its call numbers are composed of both letters and numbers. Call numbers are made up of at least two sections that encode a book’s subject and other attributes. Because of this, books on the same shelf will be about similar topics.
In library catalogs and library discovery tools like Quick Search, you’ll typically see call numbers in one long string with spaces in between each section of the call number. When call numbers are printed on the spine of a book, the sections will often be stacked in several short rows. Here’s an example of the same call number in these two different formats:
In Quick Search:
ML419 K495 S313 2006
On a book spine:
ML419
K495
S313
2006
In both formats, each section of the call number signifies a different part of the book’s code. It’s not necessary to know what these mean; the important thing is to understand how they are read and arranged.
Here are the basic rules for reading a Library of Congress call number:
- Most sections begin with letters and are followed by numbers. Letters in each section are sorted in alphabetical order before the numbers.
- Numbers in the first section are sorted as whole numbers. (In the example above, the 419 in the first section represents the whole number 419, or four hundred nineteen.)
- Numbers in later alphanumeric sections are sorted as decimal numbers. (In the example above, the 495 in the second section represents .495 or 0.495, and the same rules apply to the 313 in the third section: you read it as 0.313.)
- The final section may consist of four numbers with no letters. This is the publication year.
Using call numbers to find books
You can think of the call number as the unique address for each item that helps you pinpoint where that item lives on the shelf. Let’s say you found this book in Quick Search and want to locate it within the library:

After you’ve verified that the book is available and in the general collection, you can use the Map it tool to figure out what floor it should be on. You can also use the call number together with the floor maps (located throughout the library) to find the floor where your book should be. The call numbers are arranged in alphabetical order throughout the library’s floors. For our example, books with call numbers starting with SB are on Tier 5.
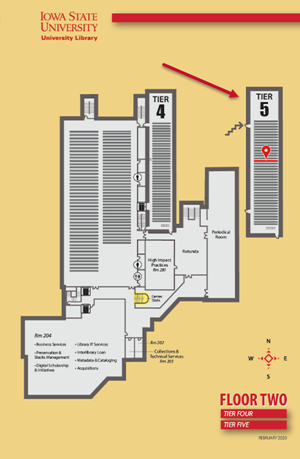
Once you’re on the right floor or tier, the next step is to find your item on the shelf by using the call numbers displayed at the end of each row of shelves. These numbers represent the first and last books in that row.

To figure out if your book is on a particular row of shelves, you first need to know if your book’s call number falls within this range. Usually, reading the first section of your call number will yield this information. You will need to understand this process even if you used the Map it tool, since that won’t show you exactly where your book is located on the shelf.
When reading the call number, start with the letters in the first section. A single letter comes before a two-letter combination starting with that same letter, so S comes before SA when you’re browsing the rows. For example, if a row is labeled with S1204 to SD504, a book with call number SB102 L36 2007 should be in the middle of those shelves, since SB falls between S and SD. In this case, you’ve found the right row and you need to find the book on the shelf.
What if multiple shelves are labeled with call numbers that all start with the same letter or letters? In these cases, you’ll need to compare the numbers in the first section of the call number to see where among the rows your item should be. Your book’s call number is SB102 L36 2007 and its first section is SB102. In the example above, our shelves have the following range: SB21 to SB123. You don’t need to look at any of the other numbers or letters in the call number yet, just focus on the beginning to find the right shelf.
As we mentioned in the previous section, the number in the first segment of a call number is sorted as a whole number. This means that 15 (fifteen) comes before 100 (one hundred). In our example, the book with a call number starting with SB102 (SB one hundred two) should be on the row of shelves with the range SB21 (SB twenty-one) to SB123 (one hundred twenty-three).
Finding your book on the shelf
Now that you’ve found the specific row of shelves your book is on, you can locate your book on the shelf! You’ll need to skim through the call numbers of the books already on the shelf to see if your book’s call number comes before or after them. This is similar to skimming door numbers when trying to locate a friend’s room in the dorms. You want to make sure you’re on the right floor and around the correct numbers to find them.
When comparing call numbers, don’t worry about reading through the entire call number every time. Instead, start at the top, work your way right and down, and look for the first place where the call numbers of the books on the shelf differ from the one you’re looking for. Did you pass where your book should be, or is it farther down the shelf?
For example, let’s say you are looking for TL799 P59 S74 2018, and run across items with the following call numbers:
- TK9 K37 1996
- TK531 K56x 1978
- TK5102 R79 2006
- TK5103 B58 2011
TL799 P59 S74 2018 starts with TL, so you don’t need to read the rest of the call number to know that this book is farther down the shelf.
Once you’ve found items that match the first part of your call number, use the second part to locate your item. Similar to the first part, this section starts with a letter or set of letters. These are arranged alphabetically. In most cases, you’ll need to find the other items matching the first letter(s) in the second part before moving to the number that follows.
Unlike in the first part of the call number, the number in the second part should be treated as though it has a decimal point in front of it, although it may not display one. Our item, SB102 L36 2007, would come between SB102 L3 and SB102 L4 because 0.36 is between 0.30 and 0.40. One way to think about the differences between numbers in the first and the second segment of the call number is that the first is a whole number, like a dollar, and the second is a decimal, like cents or change.
The final part of a call number is often a four-digit number with no letter. This represents the year of publication. Not all call numbers include a publication year, but if it is present and all other parts of the call numbers are identical, you can sort the items by putting the publication dates in chronological order. You will see call numbers that are identical up to the publication year when the library owns more than one edition of a book. Our call number, SB102 L36 2007, does have the year displayed as the last segment, but we don’t have any other editions for you to sort through.
Once you find your book, it often pays to take a look at the other items shelved nearby. Those items are often about similar topics to the item you were looking for, and may be a valuable addition to your research project.
- There are multiple rows of shelves that have the same first part as your call number: Do not despair! Move on to the next part of the call number and compare that to the same section of the labels at the ends of the rows to see if yours fits within that range.
- Your call number looks different from the examples we’ve shown: Some items don’t have typical Library of Congress call numbers. An example is TA1 Am35p. Even though it looks strange, you can still use alphanumeric order to narrow down where it should be on the shelf.
- Your book is not where you think it should be:
- Look around that area on the shelf or behind the books on the bottom shelf (it may have fallen).
- Check the reshelving area on that floor, where books used within the library are placed before being put back on the shelves.
- Check Quick Search to be sure it’s in the General Collection and that it is not checked out.
- You still can’t find your item: Ask for help at the Main Desk.

