What is a SWOT Analysis?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Strengths and weaknesses are internal to your company—things that you have some control over and can change. Examples include who is on your team, your patents and intellectual property, and your location.
Opportunities and threats are external—things that are going on outside your company, in the larger market. You can take advantage of opportunities and protect against threats, but you can’t change them. Examples include competitors, prices of raw materials, and customer shopping trends.
A SWOT analysis organizes your top strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats into an organized list and is usually presented in a simple two-by-two grid. Go ahead and download our free template if you just want to dive right in and get started.
Why do a SWOT Analysis?
When you take the time to do a SWOT analysis, you’ll be armed with a solid strategy for prioritizing the work that you need to do to grow your business.
You may think that you already know everything that you need to do to succeed, but a SWOT analysis will force you to look at your business in new ways and from new directions. You’ll look at your strengths and weaknesses, and how you can leverage those to take advantage of the opportunities and threats that exist in your market.
Who should do a SWOT Analysis?
For a SWOT analysis to be effective, company founders and leaders need to be deeply involved. This isn’t a task that can be delegated to others.
But, company leadership shouldn’t do the work on their own, either. For best results, you’ll want to gather a group of people who have different perspectives on the company. Select people who can represent different aspects of your company, from sales and customer service to marketing and product development. Everyone should have a seat at the table.
Innovative companies even look outside their own internal ranks when they perform a SWOT analysis and get input from customers to add their unique voice to the mix.
If you’re starting or running a business on your own, you can still do a SWOT analysis. Recruit additional points of view from friends who know a little about your business, your accountant, or even vendors and suppliers. The key is to have different points of view.
Existing businesses can use a SWOT analysis to assess their current situation and determine a strategy to move forward. But, remember that things are constantly changing and you’ll want to reassess your strategy, starting with a new SWOT analysis every six to 12 months.
For startups, a SWOT analysis is part of the business planning process. It’ll help codify a strategy so that you start off on the right foot and know the direction that you plan to go.
How to do a SWOT analysis the right way
As I mentioned above, you want to gather a team of people together to work on a SWOT analysis. You don’t need an all-day retreat to get it done, though. One or two hours should be more than plenty.
1. Gather the right people
Gather people from different parts of your company and make sure that you have representatives from every department and team. You’ll find that different groups within your company will have entirely different perspectives that will be critical to making your SWOT analysis successful.
2. Throw your ideas at the wall
Doing a SWOT analysis is similar to brainstorming meetings, and there are right and wrong ways to run them. I suggest giving everyone a pad of sticky-notes and have everyone quietly generate ideas on their own to start things off. This prevents groupthink and ensures that all voices are heard.
After five to 10 minutes of private brainstorming, put all the sticky-notes up on the wall and group similar ideas together. Allow anyone to add additional notes at this point if someone else’s idea sparks a new thought.
3. Rank the ideas
Once all of the ideas are organized, it’s time to rank the ideas. I like using a voting system where everyone gets five or ten “votes” that they can distribute in any way they like. Sticky dots in different colors are useful for this portion of the exercise.
Based on the voting exercise, you should have a prioritized list of ideas. Of course, the list is now up for discussion and debate, and someone in the room should be able to make the final call on the priority. This is usually the CEO, but it could be delegated to someone else in charge of business strategy.
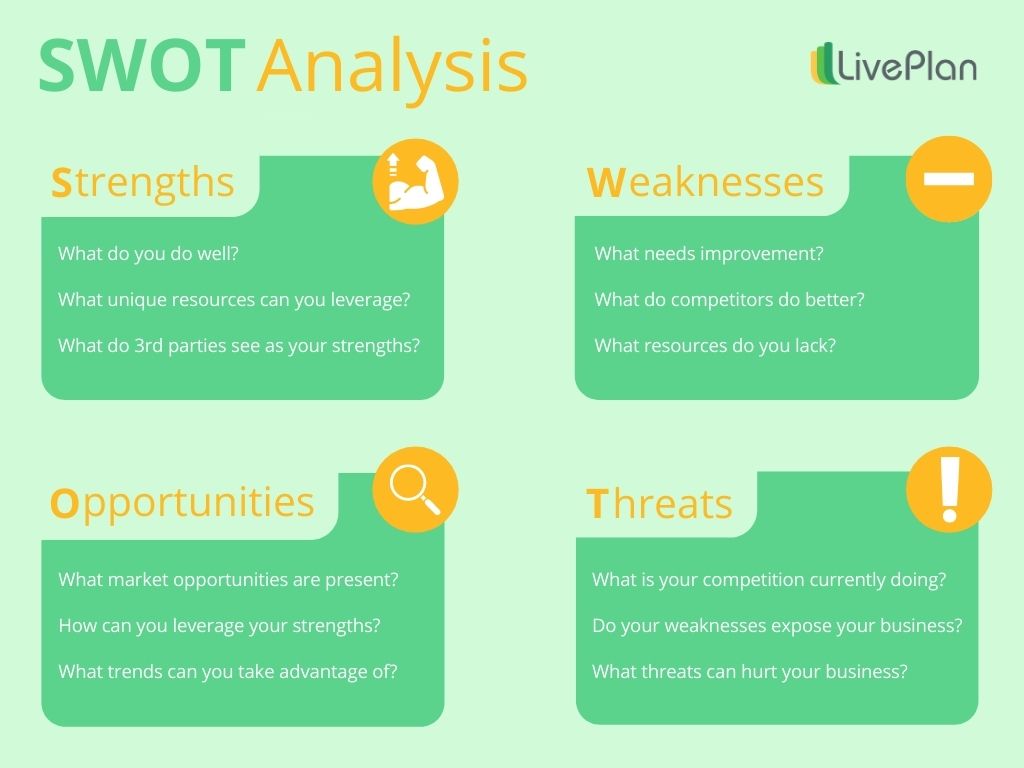
You’ll want to follow this process of generating ideas for each of the four quadrants of your SWOT analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Questions that can help inspire your analysis
Here are a few questions that you can ask your team when you’re building your SWOT analysis. These questions can help explain each section and spark creative thinking.
Strengths
Strengths are internal, positive attributes of your company. These are things that are within your control.
- What business processes are successful?
- What assets do you have in your teams? (ie. knowledge, education, network, skills, and reputation)
- What physical assets do you have, such as customers, equipment, technology, cash, and patents?
- What competitive advantages do you have over your competition?
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are negative factors that detract from your strengths. These are things that you might need to improve on to be competitive.
- Are there things that your business needs to be competitive?
- What business processes need improvement?
- Are there tangible assets that your company needs, such as money or equipment?
- Are there gaps on your team?
- Is your location ideal for your success?
Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors in your business environment that are likely to contribute to your success.
- Is your market growing and are there trends that will encourage people to buy more of what you are selling?
- Are there upcoming events that your company may be able to take advantage of to grow the business?
- Are there upcoming changes to regulations that might impact your company positively?
- If your business is up and running, do customers think highly of you?
Threats
Threats are external factors that you have no control over. You may want to consider putting in place contingency plans for dealing with them if they occur.
- Do you have potential competitors who may enter your market?
- Will suppliers always be able to supply the raw materials you need at the prices you need?
- Could future developments in technology change how you do business?
- Is consumer behavior changing in a way that could negatively impact your business?
- Are there market trends that could become a threat?
SWOT Analysis example
To help you get a better sense of what at SWOT example actually looks like, we’re going to look at UPer Crust Pies, a specialty meat and fruit pie cafe in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. They sell hot, ready-to-go pies and frozen take-home options, as well as an assortment of fresh salads and beverages.
The company is planning to open its first location in downtown Yubetchatown and is very focused on developing a business model that will make it easy to expand quickly and that opens up the possibility of franchising. Here’s what their SWOT analysis might look like:
SWOT analysis for UPer Crust Pies

How to use your SWOT Analysis
With your SWOT analysis complete, you’re ready to convert it into a real strategy. After all, the exercise is about producing a strategy that you can work on during the next few months.
The first step is to look at your strengths and figure out how you can use those strengths to take advantage of your opportunities. Then, look at how your strengths can combat the threats that are in the market. Use this analysis to produce a list of actions that you can take.
With your action list in hand, look at your company calendar and start placing goals (or milestones) on it. What do you want to accomplish in each calendar quarter (or month) moving forward?
You’ll also want to do this by analyzing how external opportunities might help you combat your own, internal weaknesses. Can you also minimize those weaknesses so you can avoid the threats that you identified?
Again, you’ll have an action list that you’ll want to prioritize and schedule.
UPer Crust Pies — Potential strategies for growth
Back to the UPer Crust Pies example: Based on their SWOT analysis, here are a few potential strategies for growth to help you think through how to translate your SWOT into actionable goals.
- Investigate investors. UPer Crust Pies might investigate its options for obtaining capital.
- Create a marketing plan. Because UPer Crust Pies wants to execute a specific marketing strategy—targeting working families by emphasizing that their dinner option is both healthy and convenient—the company should develop a marketing plan.
- Plan a grand opening. A key piece of that marketing plan will be the store’s grand opening, and the promotional strategies necessary to get UPer Crust Pies’ target market in the door.
Next steps with your SWOT Analysis
With your goals and actions in hand, you’ll be a long way toward completing a strategic plan for your business. I like to use the Lean Planning methodology for strategic plans as well as regular business planning. The actions that you generate from your SWOT analysis will fit right into the milestones portion of your Lean Plan and will give you a concrete foundation that you can grow your business from. You can download our free Lean Plan template to help you get started.
If you have additional ideas for how a SWOT analysis can help your business and how it fits into your regular business planning, I’d love to hear from you. You can find me on Twitter @noahparsons.
Third-party texts under copyright quoted in these materials are included on the basis of fair use as described in the Code of Best Practices for Fair Use in Open Education. Originally posted in Management, Growth & Metrics. Editor’s note: This article was originally published in 2018 and updated for 2021.

